| Madhans Tutorials : VLAN for absolute Beginners | |
| | |
| Objectives:
What is VLAN? VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network. VLAN is used for segmenting a LAN network. A VLAN is defined as a broadcast domain within a switched network. The following images may give an idea about VLAN. Note : VLAN is just a software configuration. No special hardwares are needed...   | |
| Why Should I segment my LAN network? • By segmenting, you create more broadcast domains and you get more bandwidth. • Additional security by isolating users according to work groups, department differentiation or even application usage without worrying about the physical location of the hosts.
| |
| How segmenting can increase the bandwdith? Each VLAN consists of a separated broadcast domain. Which means that only ports belonging to a specific VLAN share broadcasts eliminating unnecessary traffic from flooding the entire network; hence improving the overall bandwidth of the LAN. Moreover, number of messages that are to be processed by the machines are also reduced saving the valuable processor time.. The following screenshot shows a number of arp broadcast messages occupying the LAN bandwidth.
| |
| How to configure VLANs in aCisco 2950 switch?
 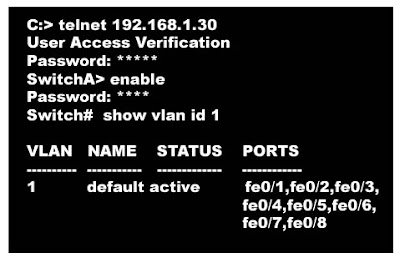 | |
| Configuration commands for a cisco switch.
 | |
| What is the Difference between "acess mode" and "trunk mode"? Have a look at the above configuration example. In this Configuration, “access mode” is used. Switch ports run in either access or trunk mode. In access mode, the interface belongs to one and only one VLAN. Normally a switch port in access mode attaches to an end user device or a server. The frames transmitted on an access link look like any other Ethernet frame. “Trunks” on the other hand, multiplex traffic for multiple VLANs over the same physical link. Trunk links usually interconnect switches. Trunks encapsulate Ethernet frames with other information to support multiplexing.
| |
| How to configure the trunk port? SwitchA(config)#interface 0/1 SwitchA(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q SwitchA(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,2,4 SwitchA(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
How to confgure the Router? Router(config-if)#no ip address (remove ip address in this interface) Router(config-if)#no shutdown Note: We are going to give different ip addresses to each sub interfaces,that is why we removed the above ip address.
Router(config-if)#int e0/0.3 (where 3 refers to vlan3) Note: Instead of 3, you can use any number. giving the vlan id is more convenient. Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 3 Note : The different encapsulation methods are dot1q, isl; here 3 refers to vlan id Router(config-subif)#ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0 Note: Assign ip address from 10.10.1.2 to 10.10.1.254 to the computers connected to this VLAN. These computers should be configured with the default gateway: 10.10.1.1 Note: Configure the other sub interfaces in the same manner. Note: Configure ACL to control the traffic between VLANs.
| |
|
Some excellent video tutorials on VLAN How Tags are working in VLAN? A video tutorial showing how to configure a cisco Switch for VLAN | |
|
Posted By : Madhan
| |
What is VLAN? , VLAN tutorial for absolute beginners, VLAN and network security.




